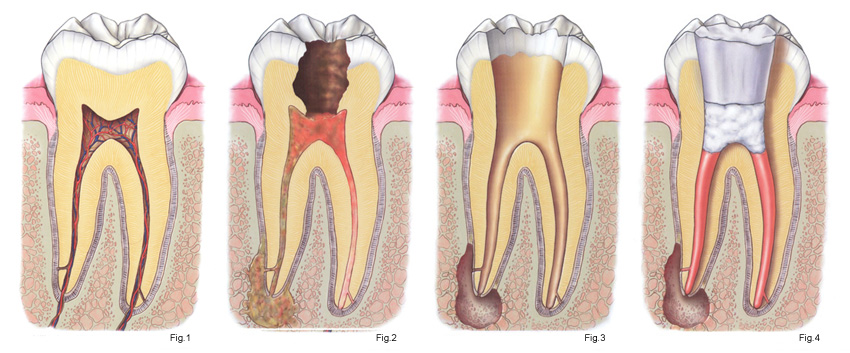
What is a root
canal
When is it
necessary?
The dental pulp, contained within the tooth, commonly indicated with the term "nerve of the tooth," is actually
a highly specialized connective
tissue containing arteries, veins,
nerves and connective
cells
Following a deep caries and related bacterial
contamination, or following a
trauma, the pulp undergoes
infection and inflammation:
is the framework, clinically often painful, of pulpitis.
The acute or chronic inflammation
(ie more or less rapid in its evolution) can propagate outside of root decay
and diffuse alveolar bone surrounding causing injury
defined as abscess, granuloma or cyst
and visible in
radiography as a 'dark area (bone loss) around the apex of the
root
.
In these cases the indication to an endodontic treatment is absolute, being the only alternative
to the extraction of the element in question.
Another indication of the endodontic treatment is the remake of a previous endodontic treatment performed poorly or failed:
endodontic retreatment.
What is endodontic treatment?
The endodontic treatment is the removal of the pulp
tissue both at the level of the
crown is at the level of the roots and replacing the removed tissue with a filling permanent
gutta percha and root
canal cement, after adequate disinfection and shaping of root canals
How long is the session?
The endodontic treatment can also be quite long especially
for molars, as it may require one or more sessions as appropriate. The operating times of
the endodontic treatment are the
following:
- Local anesthesia (the entire treatment is completely
painless and in the case of
pulp now gone in
necrosis or retreatment
anesthesia is not even necessary).
- Reconstruction of the temporary dental crown when
it is destroyed, in order to work
in optimal conditions of isolation of the operative field.
- Isolation of the surgical field through the
so-called "rubber dam". It is a rubber sheet stretched
by a metal bow and held in situ by a
metal hook
- It serves to isolate
the tooth from saliva but especially prevents dangerous ingestion or inhalation
of disinfectants and sharp instruments.
- Opening of the pulp chamber through the dental crown.
- Obtaining or
channels.
Measuring the length of each channel
(from the crown to the apex foramen of the
root) through the use of an
apex locator and an intraoral radiography. The dose of radiation absorbed in the execution of an X-ray of dental use is minimal (just think that to have an initial damage
to the lens for radiation
passing in the vicinity of the eye, are needed well
10,900 intraoral radiographs).
The risk / benefit ratio is highly in favor of
the benefit and therefore a
proper root canal therapy - Preparation of the
channels through endodontic
instruments that remove the pulp
canal, bacteria and infectious substances, creating at the same
time a cone shape, suitable to receive the
filling material washing with sodium hypochlorite, powerful antiseptic
and solvent of the protein substances (bacteria and residues pulp), to obtain an aseptic environment as possible.
Obturation
of the root canal with gutta-percha, plasticizzabile material with heat,
associated with the root canal cement.
- Temporary filling.
- Radiographic testing of the end of care.
- Reconstruction of the tooth.
Finally, especially for the premolars and molars, is strongly recommended
overcoating prosthetic crown or inlay by means of the cusps in
order to avoid the fracture coronal or root of the tooth, tooth decay and
weakened by the previous (although in minimally) by the procedures necessary
for the implementation of a correct endodontic therapy.
Will it hurt?
During the treatment the pain is completely absent through local anesthesia and even
where this is not used (teeth with necrotic pulp or retreatment) Intraoperative
pain is nonexistent. A soreness, which may be subjectively more or less slight, is almost always present in the two to three days after the root canal. Can
be addressed by any analgesic.
In very rare cases, particularly in infected
roots, because of the mobilization and the
passage of bacteria beyond the
apex, can develop an abscess,
obviously painful; the onset of these complications do not affect the success
of endodontic therapy began.
In these cases you
need to get through the drainage channels: this
can obviously run back for a few minutes in
the studio.
What you get with the endodontic treatment?
The recovery of the tooth and the possibility of
its reintegration functional
(with the prosthetic
restoration) in the dental arch.
The success rate of endodontic treatment is correct, under normal conditions, very high, very close
to 100% as almost no other
medical or surgical therapy.
The percentage decreases in the case of reprocessing, ie when the root canal has
already been made previously inadequately
(root canal fillings court, instrumentation errors, the presence of
anatomical variations, etc.).
In these cases we can perform surgery with
apicectomy el 'retrograde
filling of the root canal and this
greatly increases the chances of success.
Referance By:-
http://tinyurl.com/o8ykqup